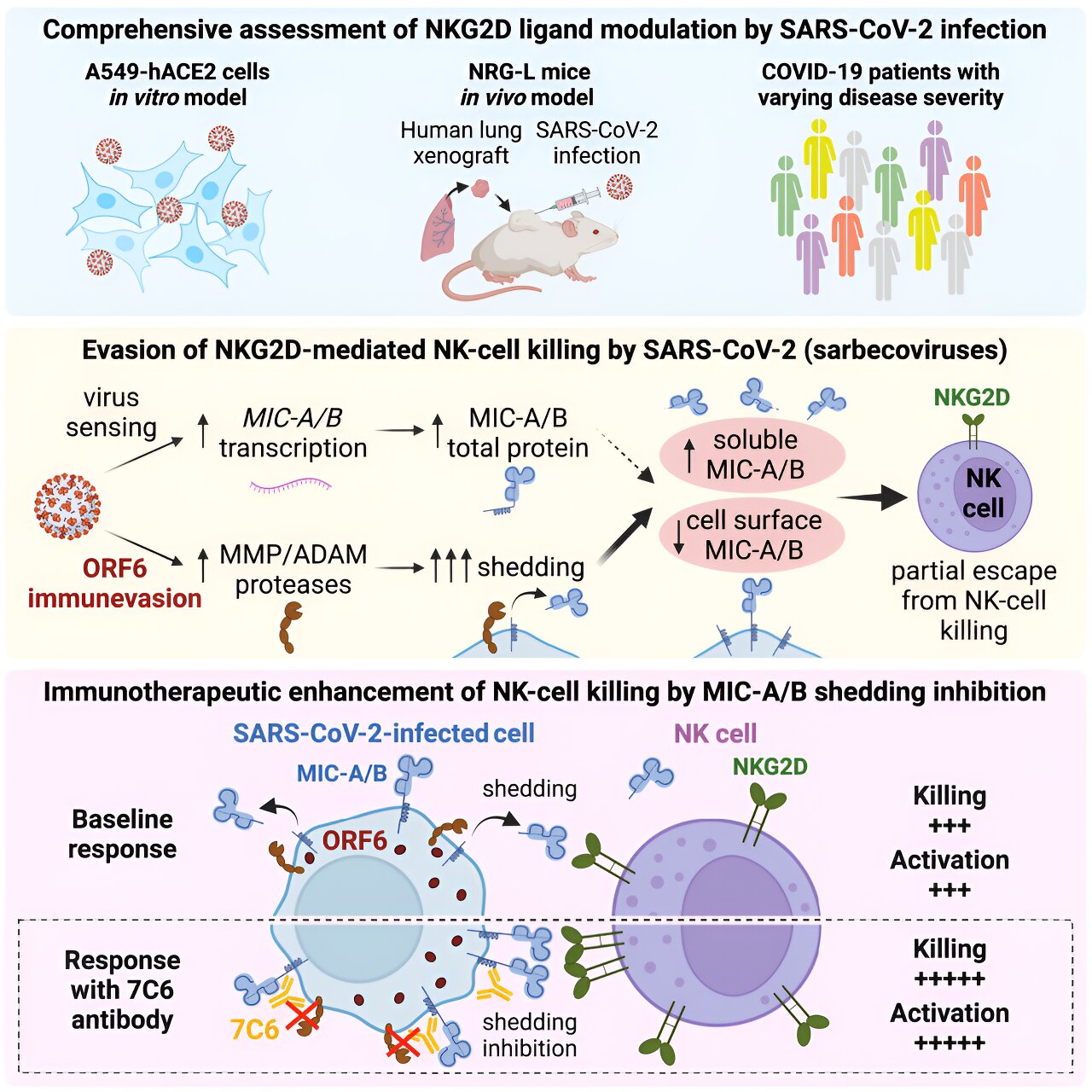
A recent study has uncovered how SARS-CoV-2 and its variants evade the immune system, shedding light on potential therapeutic strategies for COVID-19. By focusing on the interactions between the virus and the innate immune system, researchers found that infected cells reduce important immune signals that activate natural killer cells. The study identified a viral protein, ORF6, as a key player in this immune evasion process. An antibody, 76C, has shown promise in preventing this downregulation, making infected cells more vulnerable to immune attacks. The findings suggest that boosting the innate immune response could offer a promising avenue for treating COVID-19.
Source link
New study identifies mechanism of immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 and variants