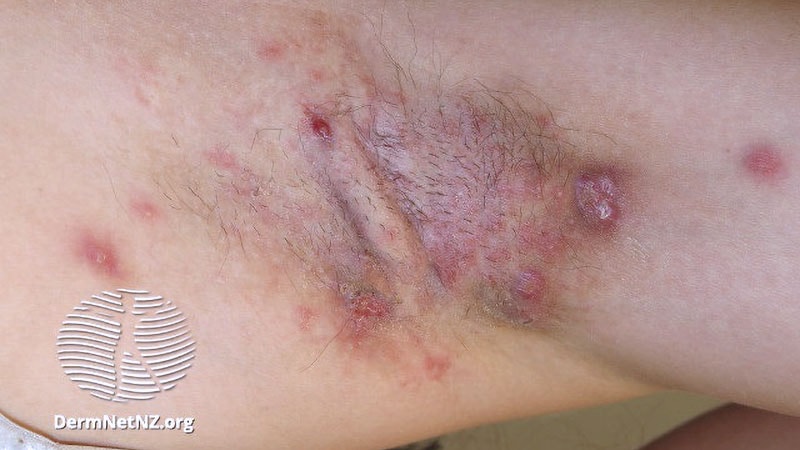
Based on his experience caring for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), dermatologist Christopher Sayed, MD, said that an exhaustive battery of tests is usually not required to diagnose early-stage HS, which can be mistaken for other conditions, such as an infection, folliculitis, and acne.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations, the diagnostic criteria for HS in general are the presence of typical lesions such as abscesses, nodules, and tunnels in classic locations like underarms, groins, and buttocks that recur over the course of at least 6 months. “There is no need for additional testing or imaging to make the diagnosis,” said Sayed, co-chair of the 2019 guidelines work group who sees patients at the HS and Follicular Disorders Clinic at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. “In many ways, the diagnosis should be very simple since the presentation is classic in most cases, though it can be confusing in the first 6 months or so.”
Persistence, Recurrence Major Clues
Prior to being diagnosed with Hurley stage I HS — characterized by recurrent nodules and abscesses with minimal scars, according to the guidelines — most people figure they’ve been getting recurrent Staphylococcus aureus infections or are having trouble with ingrown hairs from shaving, he continued. They may also say they get “boils” without an understanding of what has been causing them.
“Early HS can mimic an intense folliculitis or furuncles that can sometimes be caused by Staphylococcus infections, but the history of persistence or recurrence for months, despite treatment that should cover something like a Staph infection is a major clue,” Sayed said. “Thanks to improved resources on the internet, more patients, compared to several years ago, come in asking about HS after they’ve done their own research. As public awareness improves, hopefully this trend will grow, and patients will be diagnosed and treated earlier.” Family history is also a strong predictor of HS, since about half of patients have first-degree relatives who have a history of HS, he noted.
Clinicians can use the Hurley staging system to characterize the extent of disease and the Dermatology Life Quality Index to measure the impact of HS on quality of life. “We perform these assessments in our specialty clinic at each visit, but they are not necessary for diagnosis,” Sayed told Medscape Medical News.
The ‘2-2-6 Rule’
When she sees a patient who might have HS, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, follows the “2-2-6 rule,” which involves asking patients if they have had 2 episodes of 2 or more abscesses in 6 months. “If the patient answers yes, there’s a high likelihood that person has HS,” she said.

Hurley stage I HS is defined as nodules and abscesses without sinus tracts (tunnels) or scarring. But in Hsiao’s opinion, the Hurley staging system “is not the best way to characterize disease activity” because some patients meet criteria for Hurley stage I disease, meaning they do not have any scars or sinus tracts/tunnels, “but they have high disease activity with several inflammatory nodules and large painful abscesses that are limiting their quality of life and ability to function.”
Most cases of early-stage HS can be diagnosed in a single clinic visit, but some patients may present with a limited history of disease. For example, they may report having only had one episode of an axillary abscess or one episode of a few folliculitis-like papules in the groin. “In the absence of other physical exam findings suggestive of HS, such as open or double-headed comedones in flexural regions, I tell the patient that it is too early to call their condition HS, and I recommend that if they have another episode to call the office for an appointment for evaluation,” Hsiao said in an interview.
“What sets HS apart from an isolated incidence of a Staphylococcus aureus furuncle is the history of recurrence,” she added. To better characterize HS disease severity, she uses the six-point HS Physician Global Assessment score, a scale from 0 to 5, which classifies a patient as having moderate HS if they have five or more inflammatory nodules, or one abscess and one or more inflammatory nodule(s), without the requirement of demonstrating a scar or tunnel on a physical exam.
To help guide management decisions, Hsiao also considers asking patients with early-stage HS the following questions:
- Do you have a primary care provider (PCP)? PCPs are important care partners for patients with HS doctor to help screen for the comorbidities associated with the condition.
- What seems to make your HS worse? This can help identify potential triggers to avoid.
- What other medical conditions do you have?
- How would you describe the impact HS has on your quality of life?
- For women: Does your HS get worse around your period? “This can help to identify a potential hormonal trigger,” she said. “If the patient answers ‘yes’, I would strongly consider a combined oral contraceptive pill and/or spironolactone as part of the patient’s treatment regimen.”
‘Window of Opportunity’ to Intervene
According to Hsiao, there has been a paradigm shift in the approach to HS management that emphasizes a “window of opportunity,” where earlier initiation of appropriate long-term immunomodulator therapy is recommended to try to mitigate disease progression. The development of tunnels and scars is a telltale sign that permanent tissue destruction is occurring, and the patient’s HS is no longer mild.

Ideally, a conversation about adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, and secukinumab, an interleukin-17A antagonist (the two currently Food and Drug Administration-approved medications for HS, for moderate to severe disease/Hurley stage II/III) will have already been started with patients prior to development of a high tunnel or scar burden, signs of later-stage disease.
“Medications like this have the potential to slow and prevent that progression and reduce the surgical burden patients face over time, which is a major priority,” Sayed said. He noted that while comfort level with managing HS can vary among clinicians, “I’d encourage dermatologists to stay engaged with these patients because our training in the medical and surgical management of complex diseases like this is unmatched among other specialties,” he said. “Education of colleagues in other specialties should also be a big priority, especially for those in urgent care, emergency medicine, surgery, and OB-GYN who often encounter these patients and may be less familiar” with HS.
Besides the North American clinical management guidelines for HS, which are expected to be updated in the next 18-24 months, as well as comorbidity screening recommendations for HS published in 2022, another resource Sayed and Hsiao recommend is the HS Foundation website, which features a link to Continuing Medical Education video lectures. The foundation also hosts an annual Symposium on HS Advances. This year’s event is scheduled in November in Austin, Texas.
Sayed disclosed that he is secretary of the HS Foundation and a member of the European HS Foundation. He has also served as a consultant for AbbVie, Alumis, AstraZeneca, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, Sanofi, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB; and as an investigator for Chemocentryx, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the HS Foundation and has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, Sanofi Regeneron, and UCB; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.