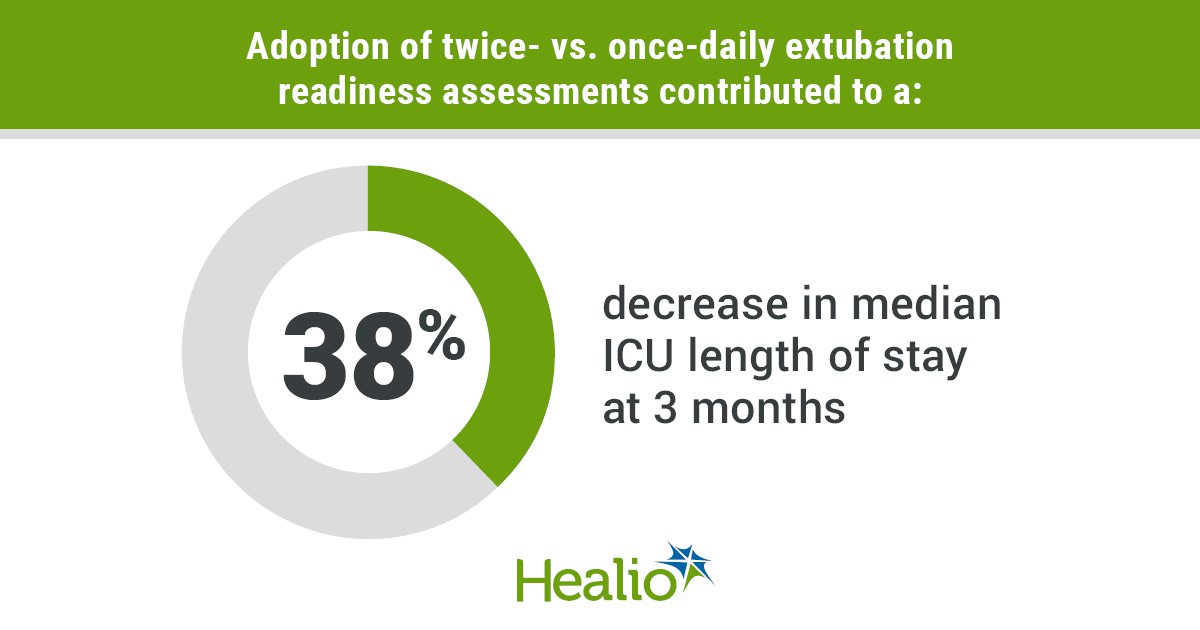
A study presented at the American Thoracic Society International Conference showed that conducting extubation readiness assessments twice a day led to a decrease in ICU length of stay for patients. The research, conducted by Julie-Kathryn Graham, found that patients in the ICU spent less time in the ICU following the adoption of twice-daily assessments. This approach also led to a reduction in length of stay for a subgroup of intubated patients. The findings highlight the importance of using evidence-based practices to optimize weaning from mechanical ventilation and improve patient outcomes. Further research is needed to assess the sustainability of these practices.
Source link
Frequent extubation readiness assessments lower ICU length of stay