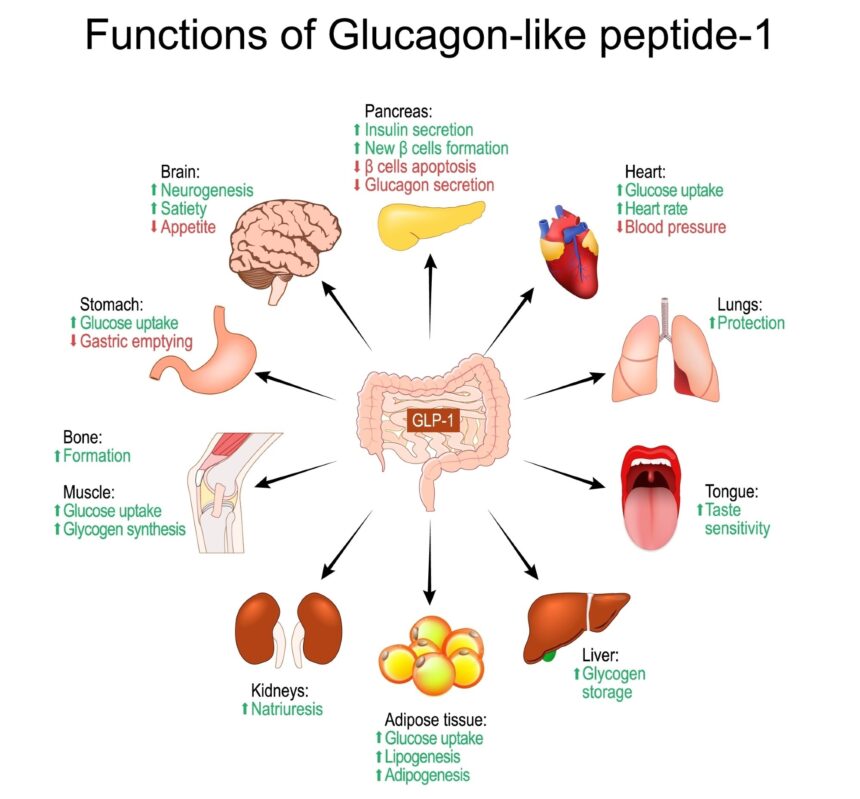
A systematic review examined the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in reducing substance use disorders. Findings from available clinical trials showed inconsistent results due to study variability and patient differences. Substance use disorders, such as alcohol, nicotine, and cocaine, are a significant public health concern, with increasing prevalence and mortality rates globally. GLP-1 receptor agonists, typically used in diabetes treatment, showed promise in reducing substance use disorders and associated weight management. However, further research is needed to understand the specific patient subtypes that could benefit from this treatment and to establish standardized protocols for future trials.
Source link
GLP-1 receptor agonists show promise in treating substance use disorders