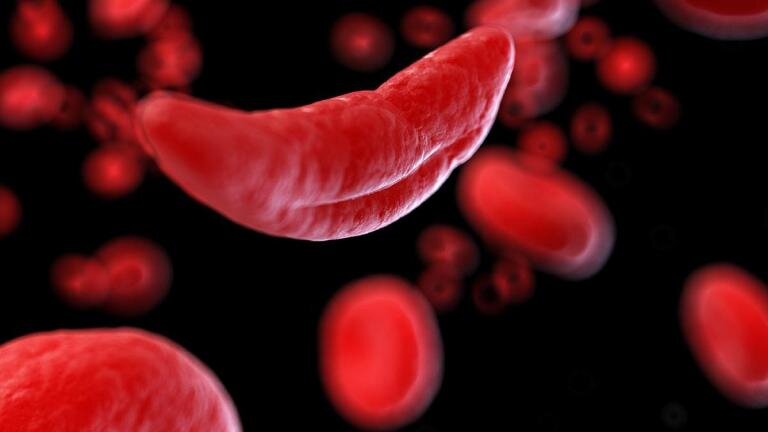
Researchers presented positive findings from the RUBY Trial, focusing on a one-time gene editing cell therapy called renizgamglogene autogedtemcel for sickle cell disease treatment. The treatment was well-tolerated with no serious side effects reported, and patients showed improvements in white blood cells and platelets. The therapy aims to correct the genetic mutation responsible for sickle cell disease. The use of CRISPR/Cas12a gene editing technology marks a significant milestone in the trial. Sickle cell disease affects millions of people, particularly African Americans. While treatments can manage symptoms, a cure is only possible through a risky blood or marrow transplant.
Source link
Novel gene-editing therapy continues to show positive results in sickle cell patients