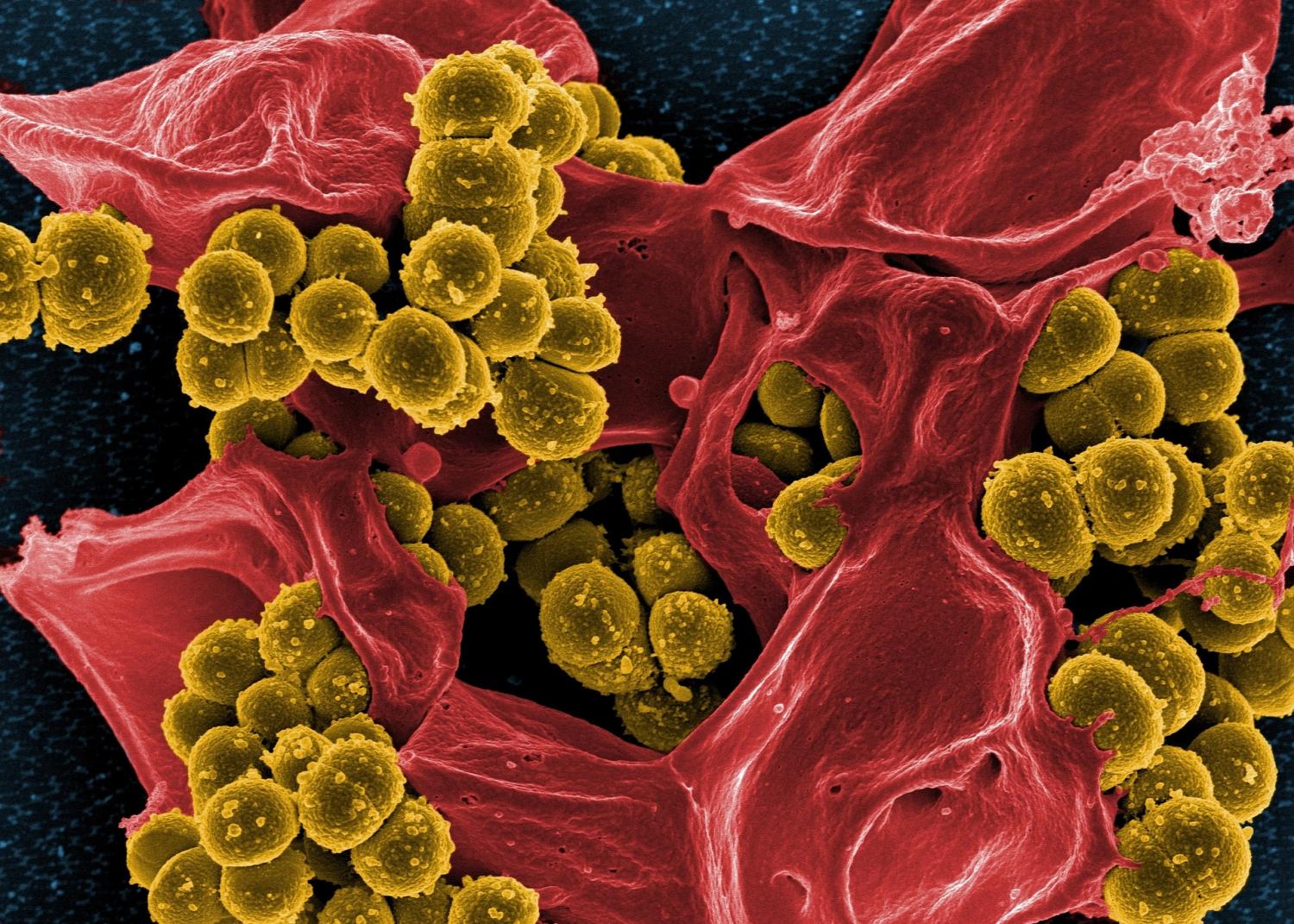
Eczema, a common skin condition, can be exacerbated by Staphylococcus aureus colonization. A study led by Anish R. Maskey, Ph.D., at New York Medical examined the use of berberine, a natural compound, to treat eczema associated with S. aureus. Berberine was found to inhibit S. aureus colonization, reduce inflammation, and alleviate eczema symptoms without adverse effects. This research shows promise for more effective eczema management, especially in cases of antibiotic-resistant S. aureus infections. Berberine’s anti-inflammatory properties and ability to inhibit mast cell degranulation make it a potential therapeutic agent for eczema. The study highlights the need for alternative treatments to address the challenges of antibiotic resistance and steroid use in eczema management.
Source link
Berberine could treat eczema-exacerbated staph infections, finds study