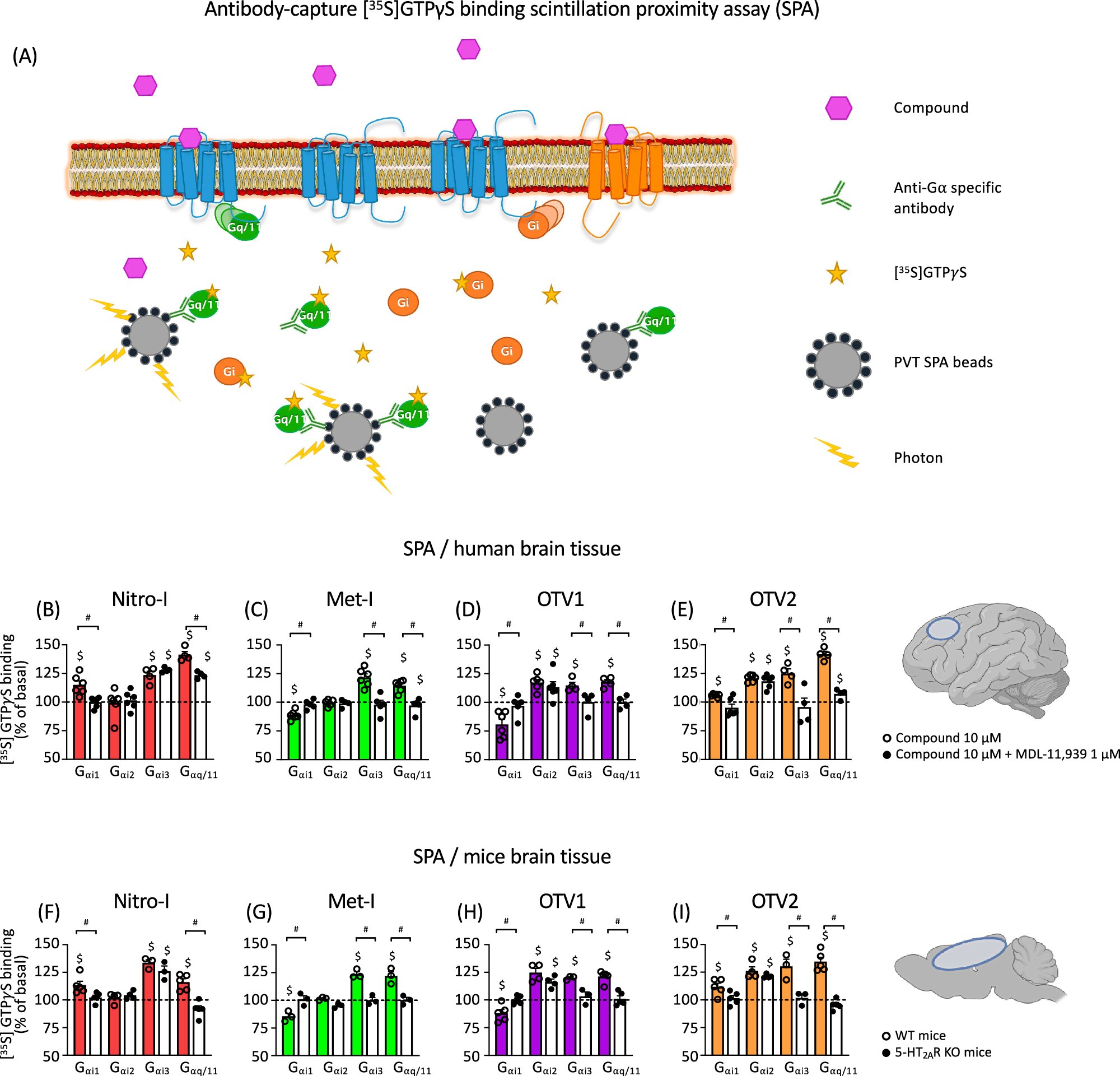
An international study published in Nature Communications suggests new personalized treatments for schizophrenia patients by targeting G proteins to modulate symptoms. Current treatments targeting serotonin receptors have side effects and limited symptom relief. The study found that specific G proteins can modulate symptoms, offering new drug development opportunities. The researchers used molecular simulations, cell studies, and human brain tissue analysis to identify compounds that interacted with G proteins. In a mouse model, these compounds showed behavioral effects specific to the activated G protein type. The study lays the groundwork for new, more targeted schizophrenia treatments with fewer side effects.
Source link
New avenues to developing personalized treatments for schizophrenia