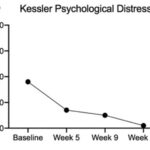
Natural compounds in gut microbiome show promise for inflammation treatment
Researchers at the University of Toronto have found naturally occurring compounds in the gut that can be harnessed to reduce inflammation and other symptoms of digestive issues. This can be achieved by binding the compounds to an important, but poorly understood, nuclear receptor. The gut microbiome hosts bacteria that produce compounds as by-products of feeding on our…